Association Between Body Mass Index and Mortality in Patients With Tuberculosis-HIV Co-Infection in Asia and Africa
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24252/al-sihah.v17i1.56107Keywords:
body mass index, coinfection, hiv infections, medline, tuberculosisAbstract
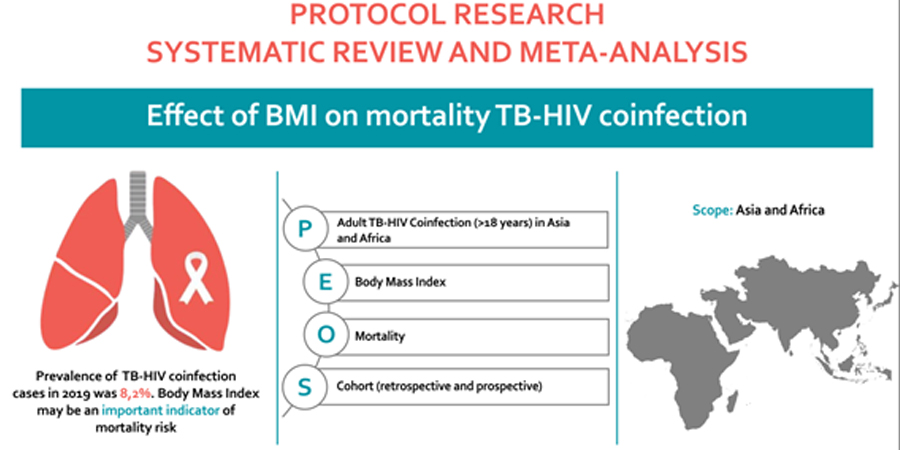
Globally, the prevalence of tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) co-infection in 2019 was 8.2%. In 2020, TB-related deaths among individuals with HIV totaled 214,000, representing an increase from the previous year. Previous studies suggest that body mass index (BMI) is a significant predictor of mortality risk in individuals with TB and HIV co-infection, as malnutrition and low BMI are frequently linked to poorer clinical outcomes. This protocol has been developed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Protocols (PRISMA-P) guidelines. A systematic review and meta-analysis will be conducted by searching three databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus, and ProQuest. This protocol aims to outline the stages and procedures of the forthcoming systematic review and meta-analysis, including the justification of the research question; the definition of Population, Exposure, Outcome, and Study design (PEOS); the inclusion and exclusion criteria; the search strategy; study screening and data extraction; and the planned data analysis. Identifying BMI as a prognostic factor through this study may inform nutrition-based interventions and treatment protocols aimed at reducing mortality among individuals co-infected with TB and HIV in Asia and Africa.
Downloads
References
Afeworki, R., Smits, J., Tolboom, J., & van der Ven, A. (2015). Positive effect of large birth intervals on early childhood hemoglobin levels in Africa is limited to girls: cross-sectional DHS study. PLoS ONE, 10(6), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131897
Alebel, A., Demant, D., Petrucka, P., & Sibbritt, D. (2021). Effects of undernutrition on mortality and morbidity among adults living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC infectious diseases, 21, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05706-z
Baluku, J. B., Namiiro, S., Nabwana, M., Muttamba, W., & Kirenga, B. (2021). Undernutrition and treatment success in drug-resistant tuberculosis in Uganda. Infection and drug resistance, 3673-3681. https://doi.org/10.2147/idr.s332148
Assebe, L. F., Negussie, E. K., Jbaily, A., Tolla, M. T. T., & Johansson, K. A. (2020). Financial burden of HIV and TB among patients in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open, 10(6), e036892. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036892
Ayenew, B., Belay, D. M., Gashaw, Y., Gimja, W., & Gardie, Y. (2024). WHO’s end of TB targets: unachievable by 2035 without addressing under nutrition, forced displacement, and homelessness: trend analysis from 2015 to 2022. BMC Public Health, 24(1), 961. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18400-5
Basnyat, B., Caws, M., & Udwadia, Z. (2018). Tuberculosis in South Asia: a tide in the affairs of men. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine, 13(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40248-018-0122-y
Bell, L. C. K., & Noursadeghi, M. (2018). Pathogenesis of HIV-1 and Mycobacterium tuberculosis co-infection. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(2), 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.128
Boadu, A. A., Yeboah-Manu, M., Osei-Wusu, S., & Yeboah-Manu, D. (2024). Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: The complexity of the comorbid interactions. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 107140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2024.107140
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mufti As Siddiq M. Irzal, Tri Yunis Miko Wahyono, Putri Novia Choiri Insani, Welstin Wemi Loa, Leopardo Alvalius Ngetwa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted to publish their work online in third parties as it can lead to wider dissemination of the work.













